Everything you need to know about skills
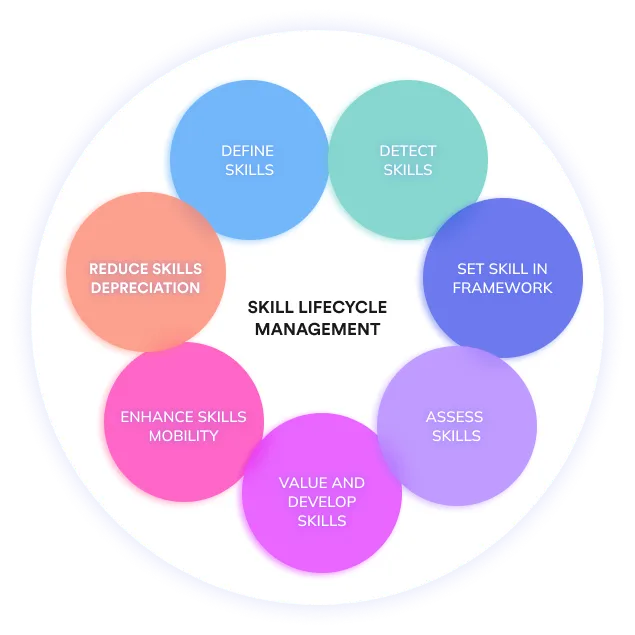
- How to define a skill ?
- How can I detect every skill in my organization?
- What are the main categories of skills ?
- How to structure your company's skills management?
- What approaches to evaluation should skills take?
- How to value and develop skills ?
- How to promote mobility of skills?
- How to mitigate the obsolescence of skills?
- FAQ
- You may also like
The skill is both a legal concept and an expression of the requirements of a profession. The use of this term within human resources dates back to the economic crisis of the late 1970s. Intended to ensure the sustainability of a company, the management of human capital expertise is now a central activity in which HR wishes to intensify its involvement.
The significant investment in this HR discipline is explained by its essential contribution to business performance. The following expressions have become part of everyday language:
- “Shortage of skills”
- “Misallocation of resources”
- “Difficulties in anticipating tomorrow’s know-how”.
- “Loss of know-how”
The life cycle of skill starts with the different definition that each company has. It ends when this faculty no longer contributes to performance. Let’s take a look at each of the stages of this still new concept.
How to define a skill ?
Skill is defined as the sum total of the knowledge, skills and behaviours that an individual uses to good effect in a given professional context.
This definition reflects the variety of information, skills and attitudes used to carry out a given set of activities.
We have good news for you: our page “How to define the skill in the company” will help you to see clearly.
How can I detect every skill in my organization?
All too often, an individual’s skills remain confined to his or her job description. While each job requires distinct professional skills, an individual’s total assets are based on all his or her experiences and interests. On a daily basis, we see how important it is to reveal assets that are too often invisible, lying dormant.
Bringing out the full potential of each individual’s skills and knowledge is one of the vocations of skills management. Our Webinar on September 29 with Implid was an opportunity to examine the priorities of our 90 participants: unleashing the full potential of every asset in the company. Neobrain has built its unique technology on several forms of AI to meet these HR expectations.
The role of AI in skills detection
Using CVs, career paths and Linkedin profiles, artificial intelligence produces a semantic analysis of an individual’s know-how. For example, this inference engine will automate the completion of employee profiles. For HR teams, it’s an opportunity to reveal all an individual’s assets, and to bring out information that doesn’t appear on job descriptions.
On average, the Neobrain Platform increases the detection of skills, data that is not always visible in a less dynamic repository. Revealing this capital of in-house expertise is one of the benefits of using AI.
But that’s not all! AI is on everyone’s lips, impacting many professions that have been protected until now, particularly “white collar” jobs.
- As a professional, we help you to anticipate these impacts on your career with a unique modeling tool.
- As an HR decision-maker, you’ll be able to model and move towards a process of continuous redeployment of resources, thus minimizing image-damaging restructuring.
What are the main categories of skills ?
At the same time, the rapid evolution of professions highlights a rapid growth in the number of new qualifications of which we are not sufficiently aware. The new professional contexts such as remote work, the digitalization of activities and tools, invite to limitthe“inflation of skills” with the help of their categorization.
Skills categories to streamline your approach:
- Behavioral skillsskills encompass interpersonal and personal skills that are not generally linked to a single job. These qualities, also known as soft skills, have the capacity to be applied in several jobs, and can be cross-disciplinary skills. Mad Skills are a form of soft skills that respond to today’s need for agility.
- Technical skills are specific to a job, they cannot be acquired without prior training.
- Industry-specific skills reflect the mastery of the issues and culture of a sector of activity.
How to structure your company’s skills management?
Once identified, companies structure their usage within a framework of reference. Today, about 65% of companies have this formal framework. Establishing a sustainable ” skillsapproach” within the company is a rigorous and participative process. The creation of business repositories and skills forming the basis of knowledge of internal assets is not a simple project, but the keystone of the future HR strategic planning.
The method for structuring skills
To organize your approach, co-construction is always the best philosophy. Workshops with operational staff from all departments help to anchor the approach in managerial practices. This collaborative work, legitimized by the General Management, offers a simple, operational skills matrix to the different departments. From then on, they have a guide to evaluate, develop and allocate their resources efficiently.
The relevance of the data chosen also depends on the existence of actors whose vocation is to ensure the integration of emerging expertise and to limit the weight of obsolete faculties: the team in charge of their governance.
What do we mean by “Governance of skills“? Read our article in collaboration with the consulting firm “Be hr” and Linnet Kotek more particularly…
Repositories as a major lever for structuring information
The maintenance and enrichment of internal knowledge repositories are subject to important methodological and technological advances. Among these, taxonomy and ontology are the most advanced classification tools. Thanks to these tools, skill becomes a common language for the various HR processes (training, mobility, etc.). An “embodied” repository reflecting concrete activities illustrated by observable facts favors the progression of the feeling of common identity.
Because most companies struggle to create, update and enrich a mapping platform, Neobrain is revolutionizing the practice. Why make things complicated when you can make them simple?
Go for pragmatism with our“AI Skills Management”” solution!
What approaches to evaluation should skills take?
Evaluating the company’s intrinsic capabilities provides a benchmark for the evolution of the company’s know-how. The employee is invited to evaluate himself, to position himself on each skill from a scale of 4 values in order to avoid the less significant intermediate assessments.
When should you formalize the evaluation of your skills ?
- During the learning process of the talent management software, in a self-declared form.
- During formal interviews such as annual assessment events.
- Following specific training to ensure their proper acquisition.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Self-Assessment:
While this model gives the employee responsibility for his or her career development, we recommend supplementing it with other sources of assessment.
Static models such as annual appraisal interviews have gradually been replaced by more regular, real-time systems.
Find out more about the advantages of self-evaluation, and the precautions to take regarding the biases inherent in the exercise, in our article “How to make a success of self-evaluation skills“.
The skill in the certification process
The amplification of company certifications (ISO 9001, BCorp, …) promised to acquire a competitive advantage, they are now a prerequisite! Certifications also have a growing benefit on the employer brand and the attractiveness of the company. Their lifespan is limited, a tool for assessing internal skills can also manage the validity of certifications.
The quality and completeness of HR data are the cornerstones of your success. Neobrain offers a wide range of tools for diagnosing, checking consistency and making data more reliable, so you can get the most out of your skills management platform.
Leading analyst G2 rates Neobrain as a Leading Solution in the Skills Management category. Here’s their matrix:
How to value and develop skills ?
At Neobrain, we focus on the “motivational ” dimension, in order to capitalize on employees’ significant assets and build meaningful career paths. This philosophy, which aims to highlight an aptitude according to the employee’s level of appetence, has several benefits:
- Better individualization of career paths
- A learning gas pedal
- Increased loyalty
Recognizing distinctive qualities by means of an ergonomic sirh is part of the challenge of building employee loyalty. Multi-source feedback, or 360°, gives new importance to the management of skills and their value in a company, since they become collective assets.
The collaborative dimension as a vector of valorization of the skills
Neobrain values the positive impact of the social dimension of its platform. The benefits for the user experience and involvement in the solution are now considered a major asset by HR teams. Neobrain gives you access to a free comparison tool to help you choose the solution that’s right for you.
Mapping skills as an HR development tool
Mapping and business bridges
This mapping makes it possible to group together the skills that can be mobilized and the resources that need to be developed, at an “instant T”, in a visualization tool. This mapping of skills is at the origin of a prospective reflection on the bridges between the different current and future roles . Our use case “Job mapping and skills” will show you how several companies have successfully adopted this practice.
This indispensable tool for modern HR management provides a framework for the management of skills and instills several other indicators:
- Measuring the gaps between the skills levels assessed and the benchmarks required for future roles.
- New areas of mobility, different from traditional patterns, which contribute to the enrichment of career paths.
- The cross-referencing of data on isolated skills and probable departures (probable turnover or retirements) provides a monitoring of the risk of loss of skill.
According to a McKinsey study in 2021 , 87% of companies say they are already experiencing discrepancies skills. Companies that succeed in bridging these gaps are those that, on the one hand, identify them and, on the other, proactively communicate current and future roles and the support offered.
Mapping and Rise in skills
The “Gestion des emplois et des parcours professionnels” (Jobs & Skills Management,formerly Strategic Workforce Planning) philosophy, combined with the “Compte Personnel de Formation” (CPF), has led to increased investment. Upskilling, Reskilling and Cross-skilling (+4% in 2023). Each of these modalities meets different objectives, and we present them to you in our “New opportunities for up-skilling” page skills.
Whether initiated by companies or employees themselves, there is a plethora of HR development paths and other measures to promote employability. VAE, coaching, skills assessments and continuing professional training are both an opportunity and sometimes an obstacle to employee orientation. Here are a few figures to illustrate the sometimes penalizing nature of the multiplicity of offers and the need for centralization:
- 40% of employees are unaware of their company’s training offer, according to our partner Edlfex.
- 71% train outside the support perimeter offered by their employer.
We believe that a strong improvement can come from a better matching of the qualifications to be supported and the training on offer. At Neobrain, each skill is allocated one or more training options to achieve the required level.
Are you thinking about setting up these assessments for your employees? Read our article “Bilan de skills : quels outils à votre disposition” before you start.
How to promote mobility of skills?
Companies rarely take advantage of this opportunity since only 6% of recruitments are internal. Employees, on the other hand, are becoming aware of the importance of mobilizing transferable skills in different job contexts.
Here are the results of a 2023 study carried out by “Les Acteurs de la skill” on the subject of professional mobility:
The Leyton Group has seized the opportunity to better address career paths through increased visibility of internal skills. Their HR Director talks to us in a webinar available here.
Even if the mobility of skills increased during the COVID period, visibility of internal opportunities remains insufficient for 73% of employees. There are several reasons for this!
- The cultural aspect is the first factor: for security reasons, external recruitment is favored over internal recruitment.
- The need to equip ourselves with a skills management systemthat can be transferred from one role to another is the second most important reason given by our customers.
- Finally, around 60% of employees consider the implementation of actions decided at annual appraisal interviews to be ineffective (source: Deloitte, HR trends).
We are convinced of the importance of cultivating cross-functionalskills . Are you familiar with them ? We tell you all about these critical assets for internal mobility in the article “skills transversales et mobilité“.
Big DATA as a gas pedal of the pragmatic mobilization of know-how
Big Data influences the various roles of human resources; recruitment, development of skills, HR management and employee career management can benefit from it. Extracting meaning and capitalizing on all HR data streams is facilitated by Natural Language Processing (NLP). Born in 1950, this multi-disciplinary field has made a considerable leap forward with the launch of the BERT language model by Google.
The scope of AI in internal job developments
From now on, the management of internal fields of expertise benefits from an intelligence capable of understanding the contextual environment that surrounds its terminology. For example, we can distinguish the differences and similarities between several jobs to compare them and build mobility areas. The relevance of matches between several “HR objects” within a dataset accelerates, and internal mobility can finally be considered a real alternative to external recruitment.
The project-based organization of companies also calls for new responses in the punctual mobilization of internal skills . Matching algorithms are accompanying the emergence of internal talent platforms. These “internal talent marketplaces” are real internal search engines equipped with filters to select the right skill and offer them the opportunity to take part in projects.
How to mitigate the obsolescence of skills?
The obsolescence of skills is the phenomenon whereby an employee is no longer able to work efficiently due to a lack of up-to-date skills or knowledge.
Four categories ofobsolescence coexist:
- The economic obsolescence of skills: skills previously used no longer have any value, no longer require mobilization.
- The physical obsolescence of skills
- Obsolescence due to organizational oversight, i.e. the company has not transferred skill when rotating its personnel.
- Obsolescence by outdated belief: today this would translate into “no need to examine the impacts of AI, we can continue to work this way without risk.”
Anticipation is therefore the best way of limiting this phenomenon, which means, on the one hand, reinforcing the Job and Career Management approach, and, on the other, involving managers and business experts in workshops and pilot projects as soon as possible.
Workforce planning as a lever for adaptation
The life of a particular skill in the company ends with their lack or loss of adaptation to a given activity. Within the framework of the Jobs & Skills Management, companies are responsible for anticipating the evolution of jobs, as well as adapting them to technological, economic, organizational and environmental changes.
Anticipating task automation
Recent trends towards digitization and the quest for sustainable business models have become imperatives for which Jobs & Skills Management is a strategic tool. Neobrain proposes to diagnose the probability of automation of jobs based on the activities they contain, and thus define a list of priorities for HR actions.
Other alternatives help to perpetuate the company’s assets and contribute to its success by improving the performance of its contributors.
What populations are the most affected by skills obsolescence ?
The employees most at risk of not being able to cope with the changes are, on the one hand, those who don’t take part in ongoing training and, on the other, senior employees. Tiphaine Brisou-Debeze, HR Director at Sage Zone Europe Sud, believes that this population is the most at risk, especially when it comes to AI and its impact on “ways of working”. Indeed, here’s a figure that tends to encourage new forms of support for seniors:
- Access to vocational training concerns 59% of the 30-45 age group, and less than 40% of the over-55s (Dares figures).
When you consider that the lifespan of a skill is dropping below 2 years according to the OECD, how can we renew our lifelong learning system?
The “sustainable development” dimension in the evolution of professions and skills
Under pressure, companies are thinking about a more responsible organization that reconciles economic performance and positive societal impact. The late appearance of this consideration by leadership stems essentially from the need to comply with legislative changes. It is an opportunity to demonstrate collective intelligence with our partners, and to develop performance criteria for our employees. This is what Nexans has been doing for the past 2 years, by integrating economic and environmental performance into the objectives of managers and teams.
Now that the ecological transition is underway in the company, another change needs to be made: that of skills to support it.
What impact will the automation of certain tasks have on your company’s businesses?
In addition to the job-destroying phenomena of globalization, there are now the risks of automation produced by predictive and generative artificial intelligence. Neobrain integrates and calculates these risks for a range of sectors and professions, and our “Strategic Workforce Planning“helps to limit these risks in advance.
Make an appointment with a Neobrain Consultant to anticipate this aspect in your Workforce Planning.
FAQ
How do I map my company's skills ?
Mapping the skills can be done through 3 main steps:
- Consolidate the available data, ensuring that it is understood in a common way across the company.
- Involve employees to enrich collective knowledge and thus visualize possible areas of mobility.
- Orchestrate each action: mobilities, trainings, resource allocation and constantly update your data.
Neobrain groups these actions in a downloadable guide.
How do you determine the skills keys to the different positions?
Defining the key skills for each position brings together several activities:
- Engage business experts and employees to reveal part of the answer
- Capture external signals through the use of an AI-centric solution
- Create a governance team to oversee all skills
How can I evaluate my employees' skills objectively and accurately?
making evaluations of skills reliable is of key importance since career paths and the choice between external recruitment and internal mobility depend on it. Several sources must make these evaluations objective:
- Involving employees in a self-evaluation or 360° evaluation.
- The contribution of managers in constructive comments
- A sum of new tools such as “serious games” and the analysis of corporate social networks.
How to encourage internal mobility through the management of skills ?
Based on skills precise employees and positions, the company reveals opportunities for internal mobility.
Neobrain is convinced of 2 complementary elements for a sustainable internal mobility culture:
- The centrality of the motivations and skills to develop these skills in the success of the courses
- The sum of mobilities is not just a new role, but the sum of opportunities such as “Gigs”, mentoring, knowledge sharing.
Do you still have questions ?
Please feel free to contact us for more information 😃














