As an HR professional, you’re witnessing a strong trend: managers are more and more actively asking their teams to acquire new skills skills. Likewise, you are undoubtedly experiencing a major wave of requests for training on emerging topics.
- How do you decide which training proposals to approve?
- How to formulate effective plans skills plans?
- How can we address the urgent challenges and opportunities presented by generative AI?
These questions, symptomatic of growing uncertainty, underline the need for a clear, actionable roadmap. Since 2015, qualification requirements for various roles have undergone a significant transformation, with an average change of 25%. This trend is accelerating, and it is projected that by 2030, the change in skills requirements will have increased by at least 65%.
So we’ve compiled a checklist for HR professionals: the top 10 skills keys to tomorrow’s performance. Our methodology combines in-depth analysis based on the evolution of our customers’ skills repositories, insights from studies published by the World Economic Forum, Pearson, Coursera, LinkedIn. We’ve complemented this with the prowess of our AI developed since 2018, which explores trends in 2 million job postings daily across the globe to offer a comprehensive view of today’s key skills landscape.
Further strengthening our approach is an in-depth study of the impact of AI on 100 professions.
What do we call high-demand skill sets?
The skills key skills in high demand refer to a combination of skills, knowledge and assets that are currently in high demand in various sectors and positions, making them skills to be developed or acquired. These skills are influenced by technological advances, economic changes and societal evolutions. They enable professionals to adapt, innovate and excel in their respective fields, making them valuable assets for their organizations. Finally, these assets often include a mix of various categories from skills : technical, technological, cognitive and interpersonal know-how.
Key factors shaping the future of skills
Understanding the forces driving the evolution of skills and know-how is crucial to staying ahead of the game. The key drivers described below not only underline the rapid pace of change , but also highlight the areas where companies need to focus their attention to foster a resilient and adaptable workforce. Let’s explore the most significant factors shaping the future of skills :
Digital transformation:
As companies undergo digital transformation, mastery of new software and digital tools hardly needs reminding. That’s not the most important thing: the speed at which digital landscapes evolve often outstrips organizations’ ability to adapt, creating a skills gap.
Perspectives on digital maturity
Companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of lifelong learning and technological fluency, but their maturity varies considerably. Some are taking the lead in digital dexterity by selecting employees with this insight, while others are just beginning to bridge the gap.
AI and automation:
The integration of AI into various aspects of work, from content creation to decision-making processes, is revolutionizing the way we work. The maturity of companies to take advantage of AI is growing.
Perspectives on the maturity of organizations in the face of AI
Leaders in this field are already reaping the benefits of AI-driven efficiencies and innovations, based on their ability to identify the right use cases. Meanwhile, others are in the early stages of exploring AI’s capabilities and looking for strategies to integrate them effectively into their operations.

Ecological Transition and Sustainability :
With the growing emphasis on sustainability and the impact of climate change, there is a pressing need for skills that prioritizes environmental considerations in decision-making processes. Companies have different levels of maturity when it comes to integrating sustainability.
Outlook on maturity in the face of ecological transition challenges
Some organizations have deeply integrated sustainability into their strategic planning and operations. Examples include the adoption of renewable energy sources, rigorous recycling programs and eco-design of products. Others are on the cusp of this journey, beginning to assess how sustainable practices can be integrated into their business models. This evolution, often seen as a constraint, also represents an opportunity. Reducing carbon footprints, improving supply chain sustainability, or engaging in corporate social responsibility programs, are subjects whose impact represents a vast field of investigation.
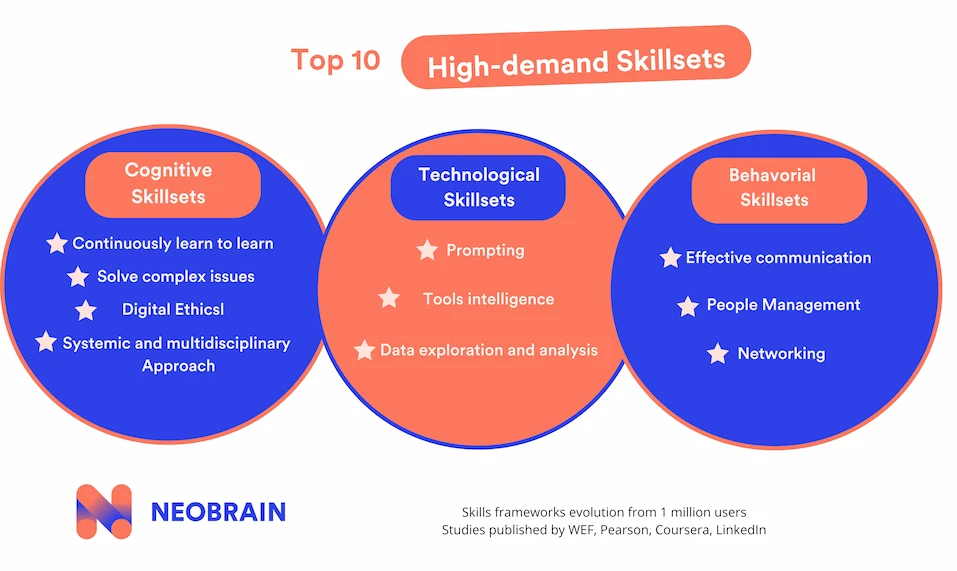
The 10 fastest-growing skills
Continuously learn to learn (Cognitive sphere)
This mindset manifests itself both in employees and through proactive organizational policies. On the one hand, employees proactively seek to grow through lifelong learning; on the other, it’s equally important for companies to cultivate a supportive culture and provide the tools and resources needed to facilitate this journey.
Despite a notable 25% increase in spending on Training and Development, as reported by the LinkedIn Learning Workplace Report 2023, 38% of employees still find it difficult to access relevant training that supports their needs. This gap leads many talents to seek open-access training opportunities outside their company’s traditional offerings. This observation highlights the need for organizations to better align their L&D strategies with employees’ learning needs and preferences.
For what jobs is this skill set expected?
- Digital marketing specialists,
- Health Policy Analysts
- Software Developers
- Educational managers
Problem solving (cognitive sphere) :
As the boundaries of traditional roles become increasingly blurred, and activities become more project-based, the ability to solve problems effectively is evolving. Indeed, it also introduces a higher level of complexity, fusing diverse know-how in a collaborative effort to bring together diverse expertise. In this context, problem-solving is about mobilizing the right resources quickly, recognizing the strong interdependence between the different aspects of the solutions envisaged.
Which jobs require problem-solving skillsets?
- Supply Chain Analysts,
- UX (User Experience) designers,
- Clinical Researchers,
- Urban planners.
Prompting (Technological) :
With the advent of generative AI, mastering the art of prompting is one of the most valuable skills skills to acquire. The ChatGPT and Bard platforms have demonstrated the significant advantages that AI can offer in terms of efficiency and innovation, and are the submerged face of a hundred mature solutions.
Currently, generative AI is taking a new step towards integration into enterprise software. This broadens the scope and usefulness of AI in the workplace, and makes it imperative for “white collar” workers to know how to interact with AI. Given the vast amounts of data these AI systems can process, the ability to create precise instructions and follow a proven methodology is invaluable. The assimilation of conversational agents within the tools themselves, as demonstrated in our video below, accelerates adherence to this new user experience. Nevertheless, the solutions developed by HRIS publishers, for example, will then require business-specific parameterization to create a tool that reflects the validated use cases.
What jobs requires in-depth knowledge of prompting?
- Content strategist
- Customer Support Specialists
- HR Recruiters
- Data Analysts
Tools intelligence (Technological)
The curiosity to continually explore and compare new tools can be a game-changer, especially for white-collar professionals, dramatically improving the efficiency and effectiveness of their production.
According to a 2021 Gartner report, it is predicted that by 2025, 70% of newly developed enterprise applications will make use of low-code or no-code technologies, a marked increase on the 25% figure observed in 2020. Staying abreast of the latest developments, understanding them and using the right tools considerably improves productivity, but that’s not all. This is a major innovation lever that IT and digital departments need to think about in order to harmonize the company’s entire digital landscape and not leave too much room for shadow IT, which concerns 80% of employees. Shadow IT usage in the cloud is estimated to be ten times higher than official cloud usage. On average, a company has 975 unlisted cloud services.
Which jobs tools do you need to keep an eye on?
- Event Organizers
- Real estate agents
- Nutritionists
- Legal
Data Mining and Analysis (Cognitive/Technological) :
This set of skills is becoming increasingly vital as professionals face the phenomenon of data or content obesity. The ability to analyze vast quantities of information, but also to discern and select the most relevant data sources from multiple information systems, is indispensable. In finance, for example, the persistent challenge is to consolidate disparate data into a single, reliable source of truth: smart data.
Finally, in various fields, the use of testing and learning approaches, such as AB testing, helps to consolidate the most effective strategies among multiple hypotheses.
Which professions require you to develop an aptitude for data mining?
- Financial Analysts
- Digital Marketers
- Clinical Researchers
- UX researchers.

Effective Communication (Behavioral) :
In a professional world characterized by simultaneous involvement in multiple projects and the prevalence of remote working, the importance of effective communication cannot be underestimated. This set of skills ensures clarity of instructions, the ability to reformulate and succinctly summarize complex ideas, and facilitates rapid decision-making processes. The ability to communicate ideas clearly and persuasively in a variety of contexts greatly enhances teamwork, leadership effectiveness and customer relations, especially when distance demands that every interaction counts.
Professions requiring skills effective communication skills:
- Social Community Managers,
- Telehealth nurses,
- E-Learning project managers,
- Crisis Communication Specialists.
Networking (Behavioral)
The ability to build and maintain strong relationships, both within and outside the organization, is invaluable. This set of skills facilitates collaboration, knowledge sharing and mutual support, forming the foundation of successful teams and projects.
Insights from industry and academia underscore the crucial role of soft skills. A remarkable Wall Street Journal survey of 900 executives reveals that 92% of them prioritize behavioral assets over technical capabilities. What’s more, in-depth research conducted by renowned institutions supports this view, indicating that a large majority of professional success is attributed to well-developed skills soft and interpersonal skills.
Careers requiring intensive maintenance of professional network:
- Business Development Managers
- Talent Acquisition Managers
- Professional coaches
- Fundraisers for NGOs
People Management (Behavioral) :
The art of effectively leading teams involves much more than simply delegating tasks. It’s about motivating and developing employees through collaborative dynamics that have recently evolved considerably (rise in the use of freelancers, remote working, blurring of strict functional boundaries, etc.).
The challenge of performance is taking on new importance at a time when productivity gains are stagnating in Europe(0.8% according to the ECB) and no longer progressing as before in the United States(3.2% Bureau of Labour Statistics). Managing means making it compatible to develop talents and inspire them to give their best. Recent insights, such as a survey conducted by CoderPad, reveal a significant reluctance among workers in the technology sector to pursue managerial roles. With 36% expressing a preference for avoiding such responsibilities, restoring the role to its former glory is a mutual quest for the HR and management tandem.
Roles for which the skills “People Management” package is critical:
- HR Business Partners
- Scrum Masters
- Health managers
- Sales outlet managers
Systemic and Multidisciplinary Approach (Cognitive)
This set of skills so-called “sustainable” skills to be acquired is a recent development, helping to meet the sustainability challenges facing the modern world. Adopting a systems approach means considering all aspects of a problem holistically, including the interactions between various components. It is particularly essential for professionals to contextualize economic systems and organizations in their complex relationships with physical constraints and human societies. This approach involves recognizing interaction at different scales, from local to global, aiming to manage the complexity of situations and anticipate the spatial and temporal consequences of actions. By integrating diverse perspectives and disciplines, professionals with this set of skills can develop comprehensive solutions that advance sustainability goals, taking a broad view that encompasses the totality of a system’s dynamics and potential impacts.
Examples of jobs requiring a systemic and multidisciplinary approach:
- Energy Efficiency Consultants
- Green Building Architects
- Supply Chain Managers
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) strategists
Digital ethics and responsibility (Cognitive/Behavioral) :
As technology, particularly AI, becomes increasingly integrated into everyday operations, understanding and applying ethical considerations in its use is paramount. This set of skills encompasses recognizing the ethical implications of digital technologies, making informed decisions that respect privacy, fairness and inclusivity, and fostering a culture of responsibility both within organizations and towards society as a whole. It addresses the need for a principled approach to technological advancement, ensuring that sustainability and ethical considerations are at the forefront of innovation and collaboration.
Roles using these new skills :
- AI Technician
- Chief Protection Officer
- Technology Policy Advisor
- UX (User Experience) designer
Conclusion
It is interesting to note that, among the different types of meta skills studied, the cognitive domain stands out as predominant, with 4 out of 10 skill sets. Human-centered skills in a world where AI is taking over is a real eye-opener.
Disseminating this know-how must take the form of a reciprocal commitment on the part of organizations and individuals, or even, at national level,a sovereignty issue, as Benoit Serre points out. Organizations create the right environment for continuous learning, while individual curiosity and dedication are key to personal growth and adaptability. For those looking to improve their strike force in this area, our platform offers a range of L&D partners who integrate with our solution ecosystem.