The skills self-assessment is an introspective exercise that enables professionals to measure their abilities, behaviors and working methods. In a professional context that increasingly values versatility and adaptability, knowing where you excel and where you need to improve should be encouraged by employers.
Consider the automotive industry: faced with a major technological shift, equipment manufacturers are moving from internal combustion engines to electric motors. For their employees, this means acquiring skills advanced technical skills, while developing soft skills such as effective stress management and rapid adaptation to new production processes. This cannot be done without measuring the starting point.
In this article, we'll explore why skills self-assessment is more relevant than ever. We'll discuss the benefits of this practice for both individuals and organizations, and provide practical advice on how to integrate it effectively into HR processes with the right precautions.
What is skills self-assessment?
Self-assessment is often an integral part of the appraisal process. It invites employees to reflect on their own contribution, providing feedback on their achievements and challenges. This self-analysis helps to identify areas for improvement, target professional development opportunities, and define future objectives.
The benefits of self-assessment
Participates in the selection of training courses
Self-assessment helps employees to clearly identify their strengths and areas for improvement, effectively guiding their choice of training courses tailored to their growing employability. The process also builds employees’ confidence, facilitating open discussions with their managers about their aspirations and coaching needs.
Data reliability and employee commitment in the workforce management software skills
Self-assessment adds an extra dimension to managerial appraisals by integrating employees’ personal perceptions of their performance and skills. This contributes to a more complete and nuanced picture of the situation This process also contributes to a better engagement of employees and managers with management tools. skills. By having several sources of data, evaluation becomes not only more objective, but also a lever for user adoption of HR technologies.
Supports annual reviews and other key talent management events
Although companies like Neobrain recommend monthly skills reviews, self-assessment remains a valuable tool for preparing formal events such as annual appraisals. Upstream assessments give managers a better understanding of their teams’ support needs, making it easier to plan and optimize development interventions skills.

The disadvantages of self-assessment
Subtleties in the definition of skills
Self-assessment requires a clear, shared understanding of the skills to be assessed. These skills, often situated in a contextual framework, vary according to the specific situations encountered in the workplace. A skill is not a monolithic block, but a mosaic of varied resources (cognitive, affective, gestural, relational) mobilized to solve problems or carry out tasks.
It is therefore crucial that organizations define precisely and uniformly what they expect from their employees, providing concrete examples to avoid any confusion.
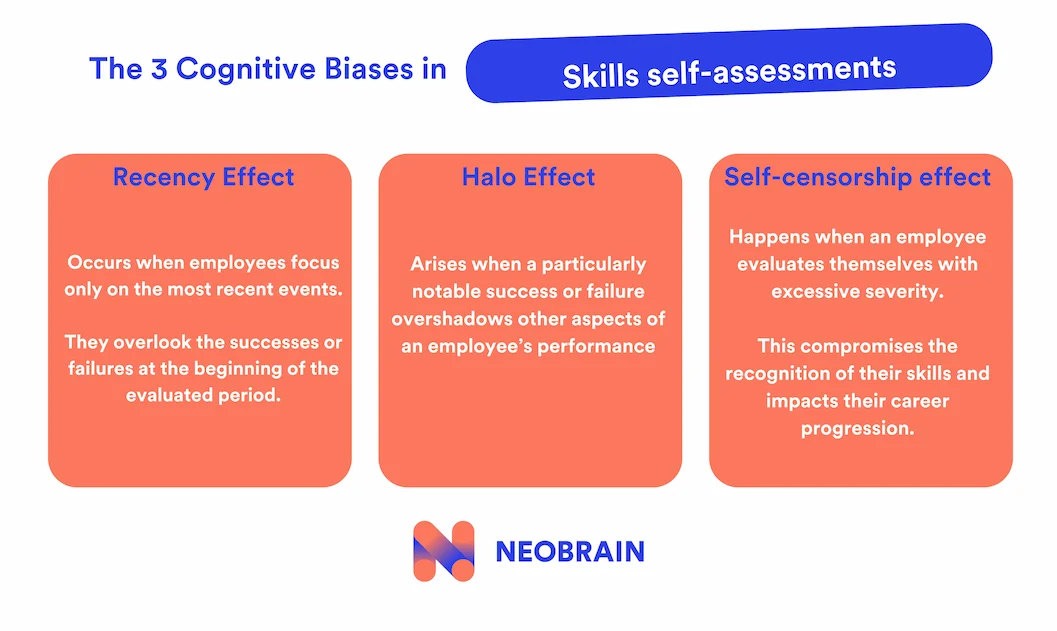
Cognitive biases in self-evaluation
What are the cognitive biases to watch out for?
Self-assessment is intrinsically subjective, and several types of cognitive bias exist: the recency effect, the halo effect and the censorship effect.
Let’s take a look at these issues and the solutions they call for:
- Recency effect: This occurs when employees focus solely on the most recent events, neglecting successes or failures from the beginning of the period being evaluated.
To mitigate this bias, it is beneficial to incorporate a chronological dimension into appraisal questionnaires, asking employees to compare their performance at the beginning and end of the year.
- Halo effect: This bias occurs when a particularly salient success or failure overshadows other aspects of an employee’s performance.
To counter this effect, it can be useful to include a summary of the period’s objectives in evaluations, and to solicit feedback on various projects and collaborations, in order to diversify focus points.
- Censorship effect: Some employees may assess themselves with excessive severity, which compromises the valuation of their skills and may affect their career development.
To limit this effect, it is advisable to train managers to recognize and balance these tendencies during performance reviews. Adding questions about necessary resources (training, job adjustments, promotions) can also help employees consider constructive improvements and position themselves in a more balanced way.
Our tips for successful self-evaluation of skills
The very design of data collection
For an effective self-evaluation process, well-designed data collection is crucial. Here are some strategies to consider:
How to design a 4-point evaluation grid?
- To maximize the effectiveness of your questions, focus on observable facts and tangible results.
- The use of rating systems, such as numbers, stars or smileys, helps employees to position themselves accurately, and facilitates comparison with managers’ assessments.
- Our customers also often ask us to add a description of what each level means in a simple sentence.
- Use a scale from 1 to 4 to encourage nuanced self-assessment and avoid the tendency to choose a median option without commitment.
Description of the skills situation:
A skill only comes to life in a specific setting, a specific situation. That’s why we encourage you to formalize them in specific work situations, without creating a “gas factory”. This helps employees to understand how their skills is reflected in their day-to-day work and in specific projects.
Enriching evaluation as you go along
Incorporate continuous training elements into the assessment so that each new training or support automatically enriches the skill levels. Using skills team levels, where relevant, can also help to objectify assessments, by providing a comparative framework that reflects performance in a team context.
A collective, long-term process
Involving more than just the manager
We see the value of involving a variety of players beyond the simple employee-manager pairing. Incorporating 360-degree feedback can considerably enrich the appraisal process by offering diverse perspectives from colleagues, subordinates and other stakeholders.
This appraisal should be visible and accessible in the skills management software, complementing manager and employee appraisals. Such an approach fosters a more complete understanding of performance and reinforces the culture of continuous feedback within the organization.
A central element in defining development objectives
A recurring good practice among our customers is to take the time, upstream, to clearly explain and position the skills self-assessment as a central element in the definition of long-term objectives, including internal mobility and career paths.
Valuing this practice is a source of alignment between individual aspirations and organizational needs, thus facilitating career planning. This requires regular and open communication about the importance of skills in professional development, ensuring that all employees understand how their progression influences their future opportunities within the company.
The impact of self-evaluation on corporate culture
Empowerment and autonomy
The skills self-assessment enables employees to proactively identify their training needs. Today, we are witnessing a form of “digital shadow“, whereby employees seek training outside the company. Introducing self-assessment leads to a refocusing of talent on internal tools, enhancing the value of these resources and adapting them over time.
Promoting a culture of continuous feedback
Studies show that companies that adopt a culture of regular, constructive feedback benefit from a 14% increase in employee engagement and a 15% reduction in turnover , compared with those that don’t.
This continuous feedback not only enables skills to be fine-tuned, but also to better align individual objectives with the company's strategic goals, thus improving overall performance.
Conclusion and future prospects
skills self-assessment is a cornerstone of employee empowerment, a process increasingly adopted in a shared and participative form in many companies. This practice is not only beneficial for aligning personal and organizational goals, but is also essential for fostering awareness and continuous development among employees.
For self-assessment to remain effective in the long term, it must become a permanent behavior within organizations and be based on clear, consensual definitions of the skills to be assessed.
In future, we recommend combining the self-declaration of skills levels with the expression of talent appetites. Recognizing not only the importance of achieving the skill levels required for talent’s day-to-day activities, but also of measuring their appetencies, is key to accelerating retention and strategic planning.