What is the state of human resources management in 2022?
In order to answer this question, Neobrain has based itself on a survey of 113 HR professionals and various recent studies, including those of McLean & Company and Gartner: we offer you a summary that will save you precious time.
4 subjects have particularly mobilized the HR teams, whatever the size of the companies:
- The attention paid to a lasting relationship with the employees.
- The energy deployed to create a link between the skills needed and the skills available.
- The major need to support leadership and managerial practices
- The increased versatility of HR in a context of digital transformation of their practices
Employee engagement as a top priority
2022 marks the continuation of the age-old fear of employee disengagement, to the point where we are now talking about the “Great Resignation“. This concern is essentially based on the significant cost of this phenomenon (97 billion euros according to Gallup). The measures taken to limit this loss of appetite have clearly not yet borne fruit, as the level of commitment remains at 21%. Going beyond initiatives that are seen as “cosmetic” by the main stakeholders and really changing leadership appears to be the only key to lasting success.
Maintain commitment and hybrid work mode
Many companies have chosen to maintain a hybrid organization following the confinements and the generalization of remote work. However, HR teams and managers fear that employees will become disengaged as a result of the decrease in office rituals and contact points between colleagues. Beyond these fears, what can be said about the hybridization of work modes ?
What is the impact of hybrid mode on productivity?
Positive: According to a quatrics report of 4,000 people, 55% of managers have seen an increase in their teams’ productivity. Eliminating commutes and reducing interruptions were highlighted as key factors in these improvements.
What impacts has the hybridization of work had on well-being?
Mixed: ⅔ of respondents in the same study say that telecommuting has increased their well-being. Yet the MLean & Company study of 1013 companies, 6% of which are in Europe, reports an increase in perceived stress. The roots of the malaise are to be found more in the blurring of personal and professional boundaries, workload, quality of relationships at work. Despite an educational effort by HR teams to limit work-related psychological disorders, RPS will be the second leading cause of sick leave in 2022.
What implications does this model have for interactions and collaboration?
Negative: ⅔ of employees felt a lack of interaction and virtual meetings are not enough as 74% of individuals prefer face-to-face meetings.
The reorganization towards hybrid work provides 2 insights into the preferred modus operandi:
- Show confidence in the autonomy of employees as long as individual objectives are defined and regularly monitored.
- Encourage, more than ever, collaborative work in order to link individual activities, which have become less visible, to overall objectives.
Learn more with our resources:
- Quality oflife at work and digital usage
- Measureand improve employee motivation.
- Fosteringcollective performance
Refocusing HR actions on job content to improve engagement
Symptomatic of a drift in the way of addressing the improvement of the quality of life at work, QWL has been replaced since March 2022 by “Quality of life and working conditions“. Too far removed from real working conditions, QWL is often criticized for having been used to facilitate employees’ lives outside of work and not in the work situation: meal vouchers and afterworks did not respond to the cases of RPS listed. From now on, the new national interprofessional agreement targets the conditions offered to achieve or not ‘good work’ in a good atmosphere, with the appropriate means.
What is the track record for employee engagement?
Mixed: Julia de Funès, philosopher and critic of the HR world thinks that “happiness at work is a managerial hypocrisy”, the period aims to “desacralize work to give it back its full meaning“. In this case, the investment in all the “extras” has, on the one hand, paved the way for increased demands from employees, and, on the other hand, distracted the HR team from the core of its activities.
By failing to address the real issues, the company has created artificial levers. From now on, it is a matter of refocusing on the quality of work content, professional trajectories, interactions at work and the evolution of management practices.
Some HRDs in our panel claim the need to “make it simpler”, such as “keeping the focus on individual motivation”.
Driven by new organizational models, service to internal customers will be refocused on developing individual skills in 2023. Indeed, many HR influencers, Josh Bersin first, are talking about a new form of organization to facilitate this return to basics: the skills centric organization.
Learn more with our resources:
The persistent imbalance between supply and demand of skills
Beyond a simple demographic issue
According to INSEE, France will continue to grow its working population until 2040, when it will reach 30.5 million, after which it will experience a significant decline in the number of working people.
This demographic aspect, which cannot be influenced, should not hide a growing imbalance between the skills available and the skills needed by companies.
The figures of the inadequacy of skills in France.
Today, the overall mismatch between supply and demand at skills has reached an all-time high with 373,100 vacancies in France, according to the French Minister of Labor, Olivier Dussopt.
- At the same time, 2.3 million people are unemployed. These figures can be challenged, however, since the calculation of part-time work is not taken into account, which would make the situation even worse.
- During the seminar of young professionals of the ANDRH, on September 30, 2022, Quentin Guilluy underlined the multiplication of fixed-term contracts “as a direct consequence of the difficulty of planning the skills needed by the company”. The figures speak for themselves: 80% of contracts signed in France are fixed-term contracts, which have increased from 8 to 12% of all contracts in the space of 5 years, and their duration has been halved in the space of 15 years to an average of 46 days.
HR teams are faced with very important uncertainties in the prediction of the business, the “Full Time Employee” or “provider/interim” therefore remains the adjustment variable. This feeds the freelancing movement and the “Gig Economy” which should count 1.5 million French people in 2030, the HR function remains reserved on this resource opportunity.
The renewal of training methods
Employees are becoming aware of the accelerated obsolescence of their skills. Technical skills, on which most training is focused, now have a lifespan of only one year. Soft skills have been emphasized to promote the medium-term employability of employees, but they remain more difficult to identify and develop with current supports. New models of rapid increase in skills are emerging, such as micro-learning and serious-gaming. Immersive virtual reality training, for its part, is now mature enough to be scaled up for certain business themes.
The majority of employees are now convinced of the need for continuous training, and 41% of them are afraid of not having the necessary skills within 5 years. 75% of them also know what skills they need(Mercer study).
The learning model is evolving towards a model where the employee is the initiator.
The training objectives are rich: reskilling, upskilling, cross-skilling; the modalities are adapted in a much more surgical way.
From now on, training programs imposed on employees without pedagogy, and outside the framework of specific career paths, are obsolete. The challenge for HR teams is therefore to implement a personalized collection of development needs, to orient training actions towards the skills critical areas while providing a sufficiently wide range of content.
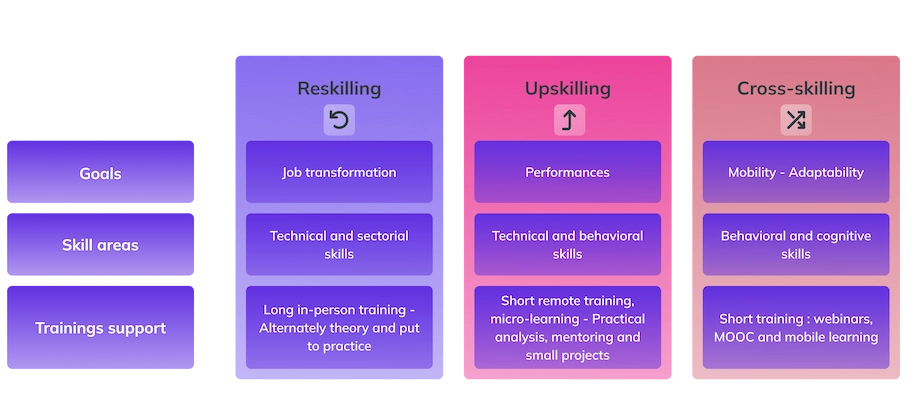
The year 2022 has thus seen the acceleration of several HR development modalities:
- Collaborative learning. Collaborators can now easily create training modules on a domain they master, and thus contribute to the collective know-how. We recommend the 360 Learning page that details Collaborative Learning.
- The use of training suggestions offered by AI. Provided by the development-oriented solutions of skills, the technology performs an association between skills to be developed and the internal catalogs.
- The notion of social sharing. Some LMS offer transparency on the training courses taken by employees in similar positions. With this information, it is possible to follow a structured and automated process to apply for these trainings.
Learn more with our resources:
- Evaluatetraining solutions.
- Fightingagainst obsolescence of skills
- Thenew opportunities for upward skills
Support for leadership and managerial practices
The need to transmit meaning at all levels
At the corporate level
Creating and animating a sense of belonging to society has always been one of the driving forces behind a company’s performance. Today, the need to adhere to a responsible corporate mission goes beyond the generational divide, and corporate social responsibility is demanded by both younger and older employees. CSR is no longer just a response to employees’ expectations but a lever for improving many processes (risk management, resource allocation).
While digital transformation is an opportunity to get closer to customers, to know them better thanks to data, and to encourage internal collaboration, “responsible transformation” leads to the gradual evolution of the company’s business.
What are the recent legal developments for HR?
- 2019 PACT
- 2020 AGEC (zero waste)
- Climate-resilience of August 24, 2021
Finally, the new CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive) will come into force in 2024. It will require each company to include in its annual report a reporting document setting out the concrete actions taken to move towards responsible practices.
Let’s take the example of BNP Paribas, which presented, during Neobrain’s CSR week, its measurement of the evolution of CSR policies among its clients. The objective is to start with an incentive approach and, in the long term, to develop a more binding policy.
At the managerial level
Wouldn’t the quest for meaning, which has been mentioned at length in 2022, be above all that of managers?
45% of them say they are morally tired of the constant changes in their organization, so the search for meaning is accompanied by a need for guidance from management.
Accompanying change is above all a matter of guiding those who drive it: HR and managers. Employees inevitably get closer to these driving forces to lead them through these periods.
It appears that their posture and skills determine the success of transformation projects:
- To be able to detect the difficulties of employees.
- To spread optimism and coherence when the injunctions can be contradictory.
- Develop new behaviors while maintaining operational performance.
Conveying meaning to collective action is not only based on the feeling of harmony with the organization’s vision; matching the aspirations, skills, tasks and trajectories of each individual are certainly the keys to management in 2023.
Accelerating the transformation of the managerial role
The quality of manager coaching in troubled times is certainly one of the major reasons whyHR professionals’ perceived effectiveness will improve (from 26% to 42% between 2020 and 2022 according to the McLean & Company report).
Historically recognized for their technical expertise on specific subjects, in 2022, HR was particularly solicited for support in changing managerial practices.
We notice that the management activity has lost its attractiveness for several years, it requires a daily support. Four reasons explain this evolution:
- Ambition no longer feeds on vertical promotion. Learning as much as possible is becoming the primary motivating factor for the new generation of talent. Acquiring cross-functional skills is considered to be a superior contribution to fulfillment compared to the responsibility of coordinating a team, a department.
- The reality of the manager’s role is becoming less legible. As the list of activities, including HR prerogatives, grows longer, its impact becomes less visible. The stress felt by some managers is not likely to encourage younger generations to take this path.
- The questioning of the real level of autonomy. Today, the question of the manager’s real autonomy arises. Wouldn’t this autonomy be based more on the organization of his own activity and that of his collaborators rather than on the definition of his objectives and the means to achieve them?
- The breakdown of the “team” cell. Finally, distancing leads managers to reinforce their capacity to individualize support while composing a homogeneous message on the meaning of collective action.
In short, managers are looking for clarification of their role and managerial practices that contribute to the internal culture. The expansion of their scope to include operational HR processes requires them to acquire increasingly technical knowledge. Collaboration with HR teams is therefore strengthened.
Learn more with our resources:
- Whatleadership for managers?
- Accompanyingthe transformation of Management
- Our5 tips for individualizing career plans
Digitalization to support HR transformation
Decompartmentalization and versatility of HR professions
The pursuit of an optimized employee experience is driving the convergence of different HR specialists toward a unifying goal. Serving the common client of the Payroll, Talent Acquisition, HR Development and Career Management departments is a source of better coordination for 73% of HR managers surveyed. It also requires a connection between each HRIS component.
To compensate for the strong control of the payroll, the HR service offering was expanded in 2022:
- 55% of HR departments have extended talent management practices to all employees. HR is looking more closely at individual preferences to offer tailored careers. This is a theme we develop in our page “How to optimize the careers of your talents“.
- Workplace and organizational flexibilityis growing in Europe and the United States. France is still lagging behind with only 6% of French companies declaring themselves open to full telework, against 22% in the US. This issue is explored in our article “How to move to hybrid work“.
- The progressive use of HR data promotes knowledge of the skills and future professions. The construction of ergonomic and reliable strategic planning tools is progressively advancing in HR organizations. Is the reliability of HR data an important issue for you? Here are the best practices: “Smart Data HR“.
The uncertainty of the economic situation in 2023 results in a limitation of team size, despite strong constraints. Statistics show:
- 1 HR professional for every 50 people in companies with less than 250 employees
- 1 HR professional for every 73 people in companies of up to 1000 people
- 1 HR professional for every 174 people in companies with more than 1000 employees.
One of the negative aspects of this insufficient staffing is the difficulty of taking the time to build improvement projects. Despite the desire to strengthen the pillars of talent management, the fatigue also extends to HR. The transversality of the skills acquired does not compensate for this exhaustion. According to the adage “the shoemaker is always the worst shod”, the HR population would like to train more in order to transform themselves more quickly. In a recent report, the ANDRH mentioned the areas in which the level of expertise should evolve as a priority:
- Jobs & Skills Management and Workforce Planning
- Succession plans
- Management of skills
- Career and mobility
The year 2022 shows that the HR population needs to improve its skills in these key areas skills , and to become acculturated, particularly in the areas of Data and Digital.
Assessment of the digital transformation of HR practices
What is the real evolution of the digitalization of the HR function?
Defined as the conversion of practices and documents to a digital format through the use of digital tools, digitalization has evolved differently in different HR fields.
According to McLean & Company, less than 50% of companies consider that they have initiated a digital transformation of HR practices. Nevertheless, 65% of them are currently preparing or implementing this evolution. The objectives are varied: to reduce dependence on the IT department, to participate in the organizational evolution of the HR department, to make data-driven decisions, etc. Each of these ambitions relies on the acquisition of skills digital and HR solutions, which are cruelly lacking in the market.
All HR processes aim to give employees and managers more responsibility. The “self-service” dimension consists of offering employees access to several HR functions. It has been designed to involve them in the management of the main processes and thus allow HR to take a higher profile on the subjects.
Digitization of HR reporting
It is one of the aspects that has seen the strongest growth. Under the weight of increasing regulatory constraints (diversity, disability, social balance sheet, equality), HR equipment has become denser, reaching 73% according to a study by the HRIS Circle. In a related field, many telework management solutions have emerged without getting a favorable response from HR professionals.
To support the employee experience issue, two other areas have been gaining favor with HR professionals this year: performance management and career management.
Digitization of performance management
Behaviors are evolving to measure and encourage performance on a more regular basis. Driven by the need for proximity between managers and employees, the tools make it possible to record exchanges and objectives, provide a shared framework for HR players and objectify performance results that are no longer debatable.
Digitization of career management
The propensity to want to know more about both skills and the emerging skills fuels the digitization of this HR practice. The evolution of the Strategic Workforce Planning to Jobs & Skills Management in 2017 coupled with professional development windfalls is instilling a desire to drive HR development and skills in a more streamlined manner. Among the top-performing companies that participated in the McLean&Company report, internal mobility is favored over external recruitment; budgetary constraints in 2023 will continue to fuel this underlying trend.
Learn more with our resources:
- Impactsand modalities of the Jobs & Skills Management
- Evaluateinternal mobility solutions
- Giving employees responsibility for managing their skills
The growing dimension of HR
Driven by the need to combat the talent shortage, the HR function has invested heavily in employee engagement and employer branding. With this pillar of performance now consolidated, it seems essential to turn to the employability of employees. The creation of career paths that respond to the skills, desired know-how and skills of the future will give a more concrete meaning to the organization’s future talents. Secondly, many analysts advocate the emergence of an organization directly based on skills to rebuild collaborative work, make the organization more agile and respond more quickly to the demands of its ecosystem. The implementation of this philosophy is based on a Talent Marketplace, which is an opportunity to implement a new vision of work, closer to the expectations of each user and to anticipate the changes in the Future of Work.
It’s time to look to the future, our HR Priorities 2023 report is now available: get inspired by our recommendations.







