The launch of Mark Zuckerberg’s Metaverse, accompanied by an investment of 10 billion dollars in October 2021, demonstrates the strategic challenge it represents. The research firm Gartner predicts that in 2026, 25% of the population will spend at least 1 hour a day in the metaverse: pure speculation or anticipation of a concrete reality?
The visible face of this investment is Horizon, a social virtual reality platform. It allows people from all over the world to meet in a virtual world. Several months after this launch, multiple uses are envisaged, it represents more particularly a revolution of the modalities of learning. Let’s detail the notion of metaverse and the new perspectives it offers for training.
What is the metaverse?
First of all, let’s dissociate the terms virtual reality, augmented reality and metaverse:
- Virtual reality : a totally simulated, immersive and interactive environment that gives the user a strong sense of presence. The individual evolves in a reality where the real environment is absent.
- Augmented reality : environment in which the individual evolves is spatially recorded in the real world but lived in a space combining real and virtual.
- Metaverse: It can be either totally virtual or combining the two realities. The difference is the large number of users simultaneously connected.
The term metaverse was first used in a 1992 novel by Neal Stephenson. This term is composed of the words “meta” (around, beyond,..) and “universe” (universe in English). This technology is not recent either, since it dates back to 2001, the number of users of the Meta platform was 300,000 in February 2022, a growth of 1000% in 3 months. According to STRIVR, a scale-up in which Workday invested in April 2002, 1.5 million users have been trained via virtual reality to date.
Examples of French companies in the metaverse:
- In the retail world, The Sandbox has 2 million active users. Retail customers like Casino or Carrefour are testing the platform to recreate the virtual supermarket.
- Manzalab has developed the teemew corporate solution to create an open and permanent meeting environment for exchanges between learners and professionals.
- Antilogy advises its clients on how to make the most of the metaverse and thus better recruit, train and collaborate.
This alternative universe requires the convergence of numerous technologies to create dynamic interactions with virtual environments, individuals embodied by avatars, and digital objects, without forgetting the security dimension of these interactions. The significant drop in the price of VR headsets (around $300) is a godsend for democratizing the use of this medium in professional training.
Why is the metaverse an opportunity for training?
Metavers such as Facebook Horizon were created to allow groups to meet while staying at home. The health crisis has strongly contributed to the development of this mode of interaction in order to stay in touch at a distance.
This technology represents, in the field of training, 3 assets:
- Saves time, no need to travel
- Comfort in the learning experience
- Elimination of inherent risks in technical training in particular.
Simply put, this technology will allow you in the future to do everything that is possible in real life, while staying at home. You’ll be able to walk around the planet, shop online, but with the same feel as you would in a store. The immersive experience will be much more engaging for employees of a company with a metaverse.
The integration of this technology into productivity platforms is already a reality: teemew will be accessible via Microsoft teams by the end of 2022.
A response to the new requirements of the future of work:
- Nomadism, the choice of one’s place of work
- Remote collaboration with an extensive network of skills
- Productivity depends on autonomy
- The quest for continued development of skills
The use of the metaverse in the rise in skills
Employees are progressing less and less through traditional training and more through real-life situations: “immersive training”. The 10/20/70 theory defines the sources of learning for an individual as follows:
- 10% through courses and academic training
- 20% during social interactions
- 70% of learning comes from contextualization of difficult tasks
However, current training programs only partially respond to the variety of modalities necessary for the permanent appropriation of new knowledge. Organizations therefore need to renew their training practices.
The estimated weight of training via this medium is around $6 billion by the end of 2022 (ABI Research estimate). In the United States, the giant Wallmart has 200 training media since 2018. Large structures such as PSA, Schneider, SNCF, Gemalto, Ingénico, Suez, Thalès, have undertaken this transformation.
What these companies have in common is that they followed a 3-step process:
- 1st stage: test & learn
- 2nd stage: scaling up
- 3rd stage: implementation of the media to the whole training in a homogeneous way
Virtual reality has already proven its effectiveness in technical training, such as learning a sequence of gestures. For example, Manpower uses virtual reality in the context of risk prevention in the workplace. Immersion in working conditions where several scenarios are proposed to learners gives excellent results. This medium is suitable for technical training and is also able to enhance soft skills of the learners.
PWC wished to deepen this postulate by a comparative study of American managers. They underwent 3 different types of leadership training: classroom, e-learning and virtual reality.
Key results include:
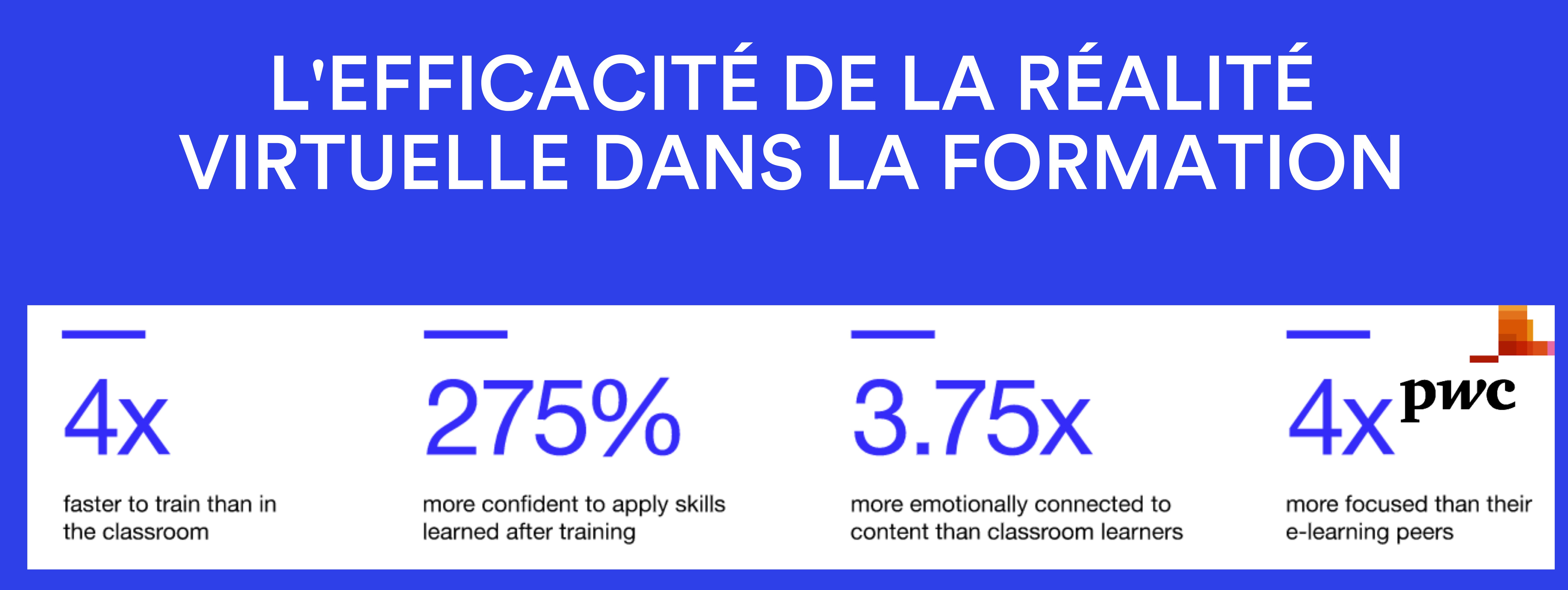
Virtual reality has an impact on 2 dimensions:
- Speed of learning
- The confidence with which learners will apply their learning
This is achieved through 2 assets:
- The higher level of emotion during training
- The level of attention needed during the training session
GAFAMs are now investing massively in virtual reality. Whether it is Meta with Oculus, which is penetrating the BtoB training market, Alphabet with VR Hub or Daydream, Microsoft with Hololens. These players have understood that the future lies inthe“Experience on Demand” and that virtual reality is one of the components of the fourth IT revolution.
Nevertheless, its cost is still a barrier to its diffusion, as Jean-Marie LESCOP, Sales Enablement Lead at Oracle, states. Virtual reality also has an interest in reducing recruitment bias (halo effect, guinea pig effect, social desirability bias).
The diffusion of this technology, apprehended by Rogers in 1995, depends on 5 elements:
- The relative advantage: this medium has empirically proven superior strengths
- Compatibility: depending on the work culture, the meta-verse may be in contradiction with existing social values and practices
- Complexity: this technology is still perceived as too difficult to implement, especially due to the lack of prior experience
- Testability : Hardware and content providers must now join forces to have the technology tested. This is what you can do in the Pavilion in Paris.
- Observability: the benefits must be illustrated in a more concrete way.
Next HR application area: employer branding!
Within a metaverse we can imagine the use of Non Fungible Tokens, for each meeting experience between a candidate and a company. Recreate the distinctive attributes of a company, promote in an immersive situation interaction scenarios that will make the recruiting company more attractive.
Metavers is one of the many opportunities, discover all these new tracks in our article“the new opportunities to rise in skills“.







